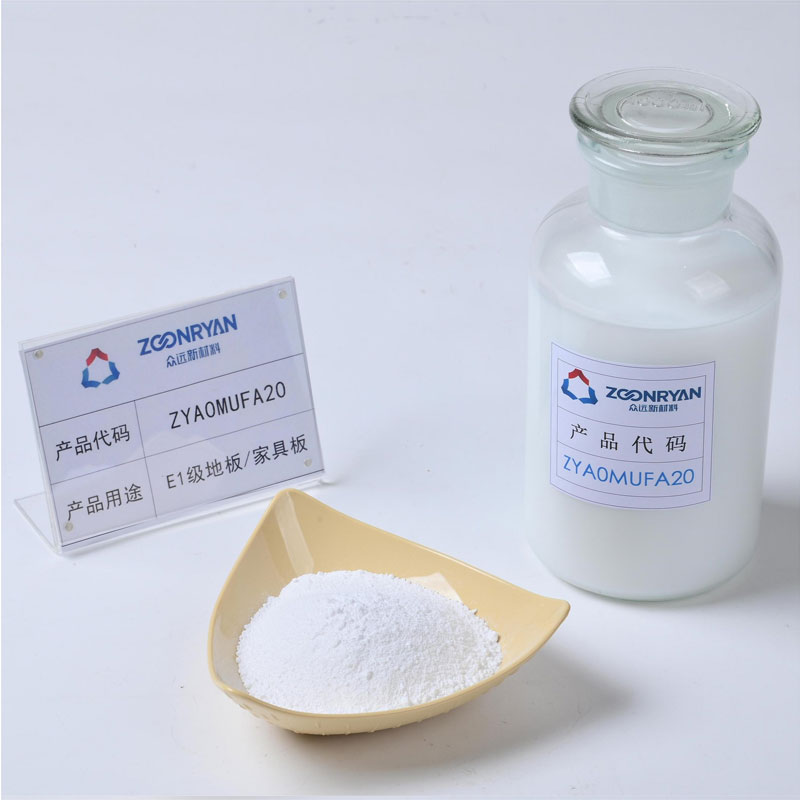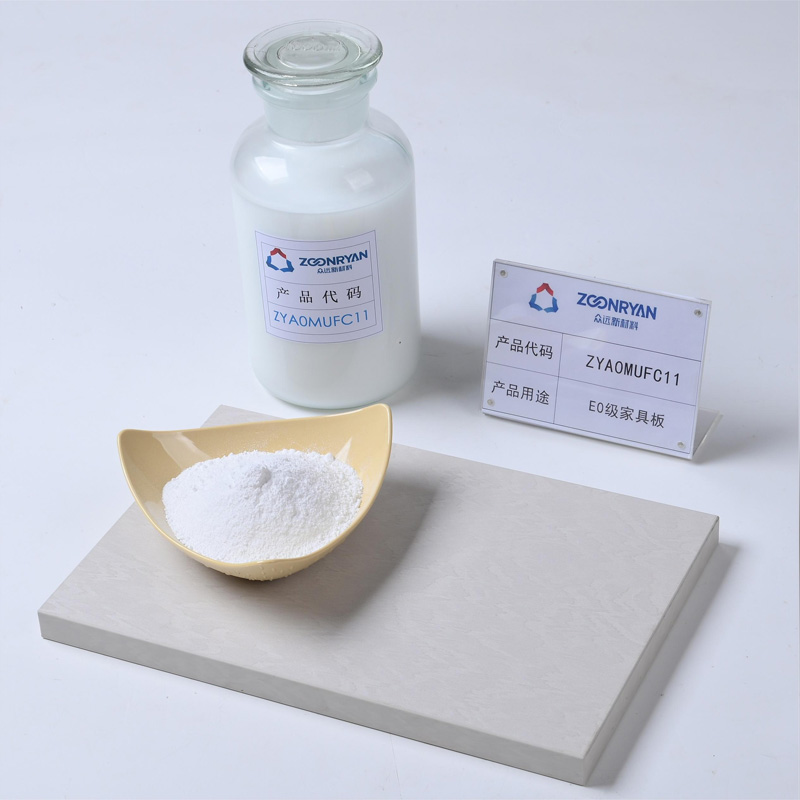
Urea-Formaldehyde Resin For Producing MDF
Our dedication to quality and excellence has enabled us to excel in the industry. Our collaborations with these MDF manufacturing facilities have allowed us to consistently provide exceptional products that meet the highest durability and performance standards."
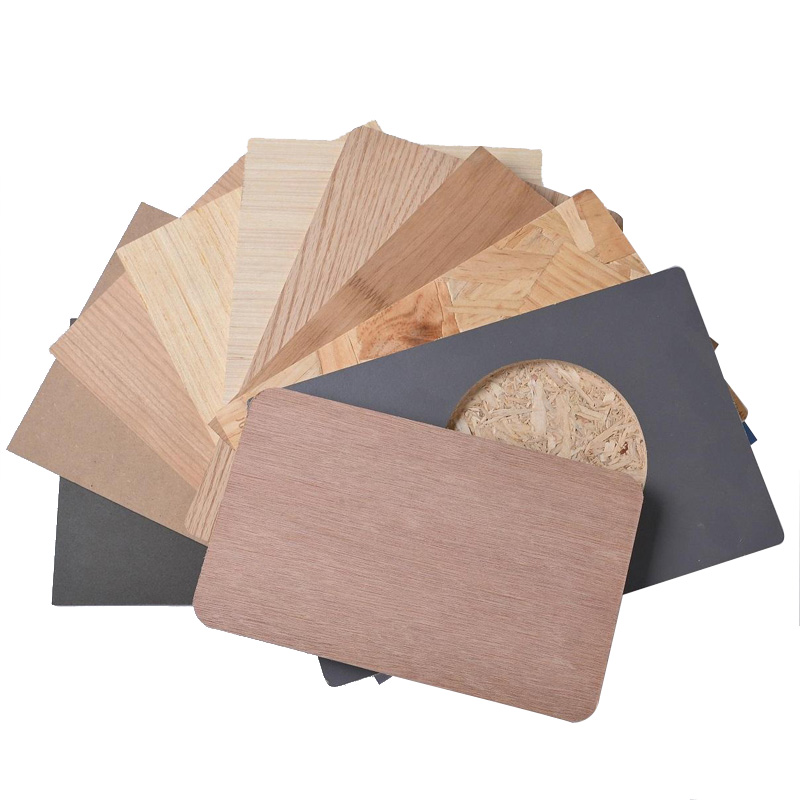
About MDF
MDF stands for Medium Density Fiberboard, which is an engineered wood product commonly used in furniture, decoration, and construction applications. It is composed of wood fibers, urea-formaldehyde resin, and other additives, compressed into uniform sheets through a process involving high temperature and pressure. MDF typically possesses consistent density, a smooth surface, and relatively high strength.
MDF is a popular choice for sheet material because it is cost-effective, easy to work with and decorate, and can be utilized in making furniture, doors, flooring, wall paneling, cabinets, interior decoration, and various other applications. Its surface can be painted, veneered, laminated, or used for various surface decorative techniques to meet different design needs. Due to its even density and texture, MDF is also well-suited for fine crafting such as carving and cutting.
Our adhesive products are designed to cater to a wide range of needs and specifications. Whether your factory demands the ultra-low formaldehyde emissions of E0, the balance of E1, or the cost-effective performance of E2, we have the flexibility to meet your exact requirements.

Urea-formaldehyde resin is widely used in the manufacturing process of Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF). Here's how it is applied:
Preparation: Wood fibers are first prepared by debarking, chipping, and refining the raw material, typically hardwood or softwood. The fibers are then dried to remove moisture.
Blending: The dried wood fibers are mixed with a urea-formaldehyde resin in a blending machine. The resin acts as a binder that holds the fibers together.
Mat Formation: The blended mixture is spread onto a conveyor belt or mat-forming machine. The fibers are evenly distributed to form a mat of desired thickness and density.
Pre-Pressing: The mat is then pre-pressed to remove excess moisture and improve the bonding between the fibers.
Hot Pressing: The pre-pressed mat is placed in a hydraulic press, where heat and pressure are applied simultaneously. The heat causes the urea-formaldehyde resin to cure and harden, forming a strong bond between the fibers.
Cooling and Trimming: After the hot pressing, the MDF board is cooled and trimmed to the desired size and thickness.
Finishing: The MDF boards may undergo additional processes such as sanding, laminating, or coating to enhance their surface finish and durability.
It's worth noting that urea-formaldehyde resin is chosen for its excellent bonding properties, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce consistent results in MDF manufacturing. However, it's important to ensure proper ventilation and handling precautions during the manufacturing process due to the potential release of formaldehyde gas, which can be harmful if not managed appropriately.

















